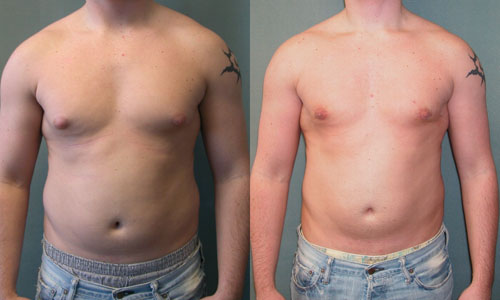
Gynecomastia is a common condition in men and boys. The breasts swell and become abnormally large. All men and women have breast glands, but they are not noticeable in men, because they tend to be small and undeveloped.
Gynecomastia does not mean that someone has extra fat from being overweight. It is caused by additional breast tissue. Doing exercise or losing weight will not reduce the breast tissue in gynecomastia.
Pseudogynecomastia is a separate condition, where fat builds up in the breasts, possibly due to being overweight or obese.
Surgery for Gynecomastia
The breast consists of glandular tissue, which is firm and dense, and fatty tissue, which is soft. The ratio varies between individuals. A man with gynecomastia may have too much of both types of tissue. Liposuction can remove excess fatty tissue. It involves inserting a small tube through a 3- to 4-millimeter incision. Excision means cutting out tissue with a scalpel, to remove excess glandular tissue. This will normally leave a scar around the edge of the nipple. If a major reduction in tissue and skin is necessary, the incision and the scar will be larger. In some cases, both excision and liposuction will be used. After surgery, the chest will be bruised and swollen, and the patient may have to wear an elastic pressure garment for 2 weeks to help reduce the swelling. It will normally take about 6 weeks to return to a normal routine. Complications from surgery are rare. They include insufficient removal of breast tissue, uneven contour to the chest, and reduced sensation of one or both nipples.

